|
Feedback Form
| Introduction | Design | Ideas | Design & Control |
Project Suggestions |
| Design Process | Design Brief | Evaluation | The Design | Design Review |
| Page 1 | Page 2 | Page 3 | Page 4 | Page 5 |
How can you get out of a rut in Roamer Design?
 |
 |
| Change the basic shape. | Give the Roamer a trailer |
 |
|
| Change the basic colour. | |
 |
|
| Make the Roamer into a body, not a head. |
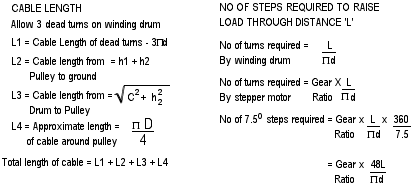
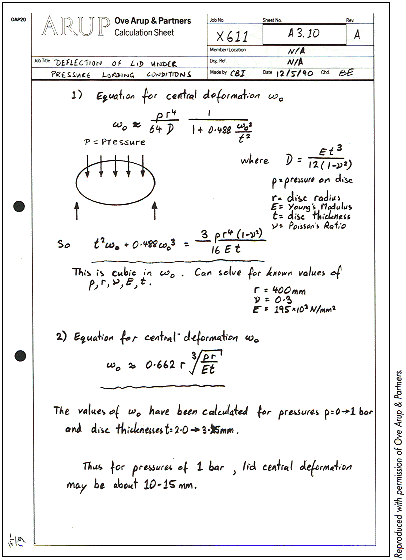
Design Calculations
Most designers work intuitively. Yet design, particularly engineering design, can involve mathematical, scientific or technological calculations. Good professional designers can support their intuitive flair with calculation and vice versa.
Design calculation may provide useful educational opportunities for older pupils. By providing a practical problem solving context, Roamer design can make mathematics meaningful. The simplest calculations illustrate how vital mathematicsis in modern technology and how essential the skill is to some types of designer.
 |
||||
| Structural engineering designers are frequently involved in stress and strain calculations. However, they do develop an intuition which enables them to predict answers to very complex problems. Sometimes they estimate the size of a structural member and check its suitability by calculations. Other times they check their calculations by intuition. | ||||
|
||||
|
Alternative Designs
|
Generating Alternative Designs It is good design practice to devise more than one Basic Design. These are evaluated to see which is the most suitable for further development. Older children should be encouraged to adopt this approach. |
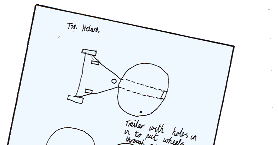 |
 |
|
|
Appraising Basic Designs Proposed designs should be judged on their ability to fulfil the Design Brief. During evaluation the designer will consider factors not stated explicitly in the brief. For example, a designer would automatically appraise a design on its manufacturing simplicity even if this was not stated specifically in the design brief. (Also see Design Factors). Appraisal should be tried even by inexperienced pupils. It helps to clarify what they are expecting and make comparisons with the final design.
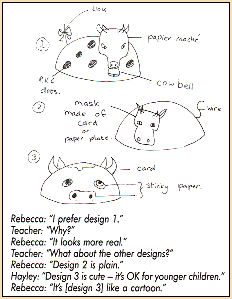
This transcript illustrates how teacher-led discussions can be very beneficial in helping pupils to clarify their expectations. |
Transcript of appraisal discussions of a group of junior school children looking at different design ideas for a cow.
|
A Formal method for Appraising a design
Older children may try a formal evaluation method. The options for a Roamer Rescuer were evaluated using this approach.
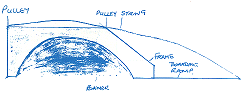
Roamer Rescuer: Pick-Up Ramp Design
Appraisal criteria were considered to be:
| Roamer Rescuer: Pick-Up Ramp Design | ||||
| Criteria | Weighting | Score | Weighted Score | Comments |
| Locate Breakdown | 2 | 1 | 2 | Could be difficult to get boarding ramp in right place. |
| Pick-up breakdown | 3 | 2 | 6 | Simple mechanism |
| Drag breakdown | 3 | 2 | 6 | Keeping breakdown on ramp may be a problem |
| Programming | 2 | 2 | 4 | Involves Control programming |
| Speed of recovery | 1 | 2 | 2 | Locating breakdown could be slow. |
| Manufacture | 2 | 3 | 6 | Simple to make |
| Cost | 1 | 3 | 3 | Simple design = low cost |
| Total | 29 | |||
| The design criteria are classified as to their importance: | How well the design complied with each criterion is scored: |
| 0 - Unimportant 1 - Useful feature - Achieve if possible. 2 - Important feature. 3 - Essential feature. |
0 - Does not satisfy the criterion. 1 - Moderately satisfies the criterion. 2 - Satisfies the criteria very well. 3 - Completely satisfies the criterion. |
The viability of the design is calculated. The design with the highest total is selected. Any design rating 0 for any of the essential factors is automatically precluded.
| Evaluation of Roamer Rescuer: Drag Line Design | ||||
| Criteria | Weighting | Score | Weighted Score | Comments |
| Locate Breakdown | 2 | 3 | 6 | No precise movement required |
| Pick-up breakdown | 3 | 3 | 9 | Simple mechanism |
| Drag breakdown | 3 | 3 | 9 | Experiments show this method ofdragging works well. |
| Programming | 2 | 3 | 6 | No complex programming |
| Speed of recovery | 1 | 3 | 3 | Will be as fast as possible if route around Roamer is kept to a minimum. |
| Manufacture | 2 | 3 | 6 | Simple to make |
| Cost | 1 | 3 | 3 | Simple design = cheap cost |
| Total | 42 | |||
Drag Line Design
Formal appraisal of Roamer Rescue designs by pupils from King Edward VI School serves to illustrate a number of key points.
- The Drag Line Design is an excellent example of an'out-of-the-rut' design solution.
- Its simplicity makes it an easy winner.
- If the criterion "Move the Roamer to any location" is considered essential then this design could score 0 and would be rejected.
Careful choice of ihe appraisal criteria is essential.
This technique can be hard for the inexperienced pupil. But the process of formal appraisal provides an excellent record of the pupils thinking and can be used to assess which design assumptions worked and which didn't.
| Back to top |
|---|